How Do RFID Wristbands Work? A Clear and Complete Guide
Introdu
If you’ve visited a modern hospital, attended a music festival, or stayed at a high-tech resort, you’ve likely encountered RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) wristbands. These smart bands have quickly become widely adopted because they offer secure, fast, and fully contactless identification—an upgrade from pa
Their main purpose is to manage high-volume environments efficiently, whether it’s patients who require coordinated care or thousands of attendees entering a large event. Disposable RFID wristbands, in particular, are now optimized for large-scale operations, providing a smoother user experience and greater cost efficiency than traditional barcode systems.
But how does a wristband that works with just a tap actually function? This guide explains the principles of RFID wristbands and why they are transforming identification in high-traffic settings.
Technical Breakdown: How Do RFID Wristbands Work?
1. The Construction of an RFID Wristband

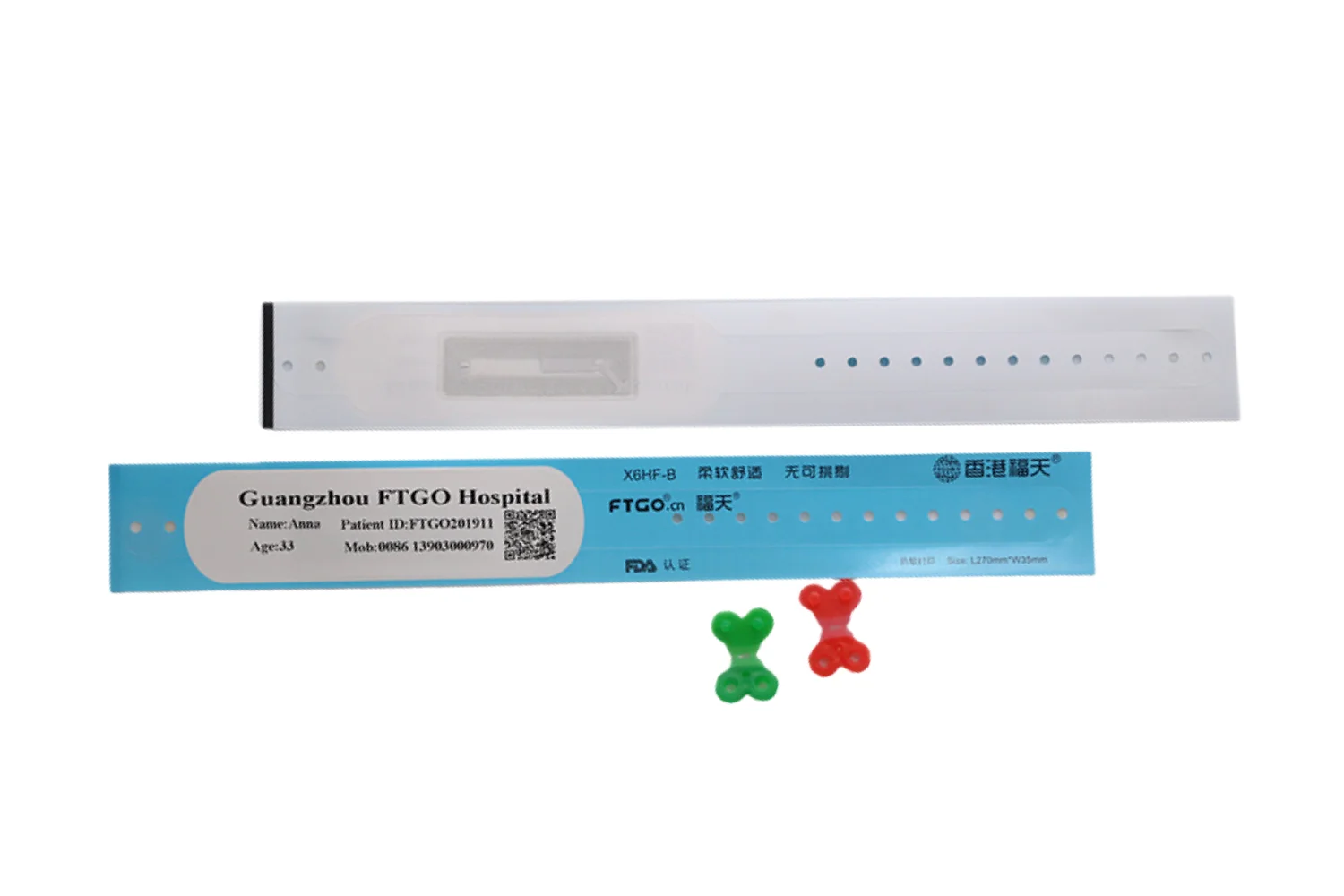
RFID wristbands look similar to regular bands but contain an embedded electronic component made of:
RFID Chip (Tag): Stores essential data such as a unique ID, access permissions, account balance, or user information.
Antenna: Sends and receives radio signals between the wristband and the RFID reader.
These components can be embedded in various materials including plastic, nano-silicone, vinyl, fabric, or composite bands, depending on durability needs.
2. Types of RFID Tags
There are three common tag types:
| Tag Type | Power Source | Working Principle | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive | No battery | Powered by the reader’s RF field | Most event wristbands & patient wristbands |
| Active | Built-in battery | Continuously transmits signals | Real-time asset tracking |
| BAP (Battery-Assisted Passive) | Small battery | Activated only when close to reader | Specialized long-range systems |
For wristbands, passive HF (13.56 MHz) tags are the industry standard due to short-range security and fast data transmission.
3. The Three Core Components of an RFID System
An RFID identification system includes:
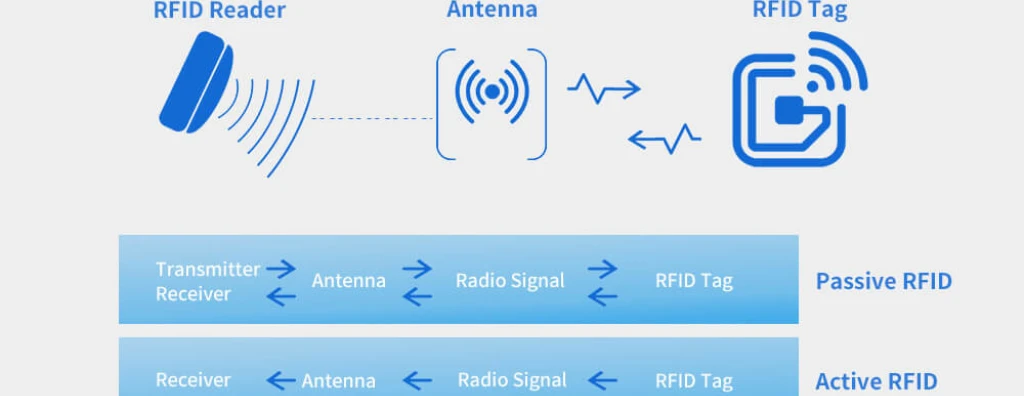
Tag: Chip + antenna embedded in the wristband
Reader: Sends radio signals to activate the tag and receive data
Software: Manages encryption, access control, and event logging
These components work seamlessly to deliver reliable, contactless identification.
4. The Contactless Working Mechanism
The process occurs in milliseconds:
The wristband moves close to the reader.
The reader emits a radio signal.
The tag’s antenna captures the signal and powers the passive chip.
The tag sends its stored data back to the reader.
The software verifies and records the interaction.
This “tap-and-go” experience is what makes RFID ideal for crowded environments.
5. Why HF (13.56 MHz) Is the Standard
High Frequency (HF) RFID offers the best balance for wristbands:
Short-range communication enhances security
Fast transmission speeds up access verification
Stable performance in environments with many people and devices
This is why HF is used in both patient wristbands and event wristbands.
What Data Can RFID Wristbands Store?

Compared to barcodes, RFID wristbands offer far greater data flexibility. A typical passive RFID tag can store up to 3 KB, while some UHF tags can store up to 8 KB for advanced applications.
Common stored data includes:
Unique ID
Access levels
Credits or prepaid balance
Points or loyalty data
Guest information
Patient identifiers
Allergen notes or restrictions
This enables more complex systems without requiring physical updates to the wristband itself.
Security and Flexibility
All communications between the tag and reader are fully controlled by the backend software:
Data is encrypted, preventing unauthorized access
Access rights can be updated in real time
Systems can log every interaction for accurate tracking
This makes RFID suitable for sensitive environments and dynamic access control.
RFID Wristbands vs. Barcode Wristbands
Although both store data, the functional differences are significant:
| Feature | RFID Wristband | Barcode Wristband |
|---|---|---|
| Reading Speed | Very fast; many tags per second | Slow; one at a time |
| Line of Sight | Not required | Required |
| Automation | Works with gates & checkpoints | Manual scanning |
| Read/Write | Supports updates | Read-only |
| Durability | Water-resistant, heat-resistant | Easily damaged |
| Security | Encrypted, hard to duplicate | Easy to copy |
| Best Use | Large events, secure access control | Basic identification |
This comparison explains why large hospitals and major events are transitioning to RFID-based systems.
The Transformation: Efficiency and Cost Benefits
1. Faster and Smoother Operations
Speed: RFID’s non-contact scanning reduces queue times and delays.
Accuracy: Less manual handling results in fewer administrative errors.
2. Cost-Effective for Large Quantities
Disposable RFID wristbands designed for single use are engineered for large-scale operations.
They provide advanced identification capabilities at a practical cost per unit.
3. Flexible and Customizable
RFID wristbands can be customized for different environments:
Printable thermal RFID wristbands
Fabric RFID wristbands for multi-day events
Plastic and silicone RFID wristbands for repeat-use settings
This ensures the right fit for any event, venue, or facility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between RFID wristbands and NFC wristbands?
Both use radio-frequency technology, but:
RFID supports short or long read ranges depending on frequency (HF/UHF).
NFC only works at very close range (a few centimeters) and is compatible with smartphones.
NFC is best for mobile interactions; RFID is better for large-scale identification.
2. How much more expensive is an RFID wristband compared to a regular disposable wristband?
RFID wristbands cost more because they contain a chip and antenna.
On average, they are several times the price of basic disposable wristbands, depending on:
Chip type
Material
Frequency
Printing/customization
3. Can RFID wristbands be customized?
Yes. Common customization options include:
Material (silicone, fabric, vinyl, plastic)
Color and printed design
Chip type (LF/HF/UHF)
Shape or size
Encoding or pre-programming
Customization varies depending on the application.
Conclusion: Ready to Upgrade Your Identification System?
RFID wristbands operate through a simple combination of a chip, an antenna, and an RF signal—but the impact is significant. They enable secure, fast, and data-rich identification that improves efficiency and reduces operational errors.
For high-volume environments such as hospitals and events, RFID wristbands offer a practical and modern upgrade from traditional barcode systems.
Share this article
Follow us
A quick overview of the topics covered in this article.
- вводить
- Технический анализ: как работают RFID-браслеты?
- Какие данные могут хранить RFID-браслеты?
- Безопасность и гибкость
- RFID-браслеты против браслетов со штрихкодом
- Трансформация: эффективность и экономическая выгода
- Часто задаваемые вопросы (FAQ):
- Заключение: Готовы обновить свою идентификационную систему?










